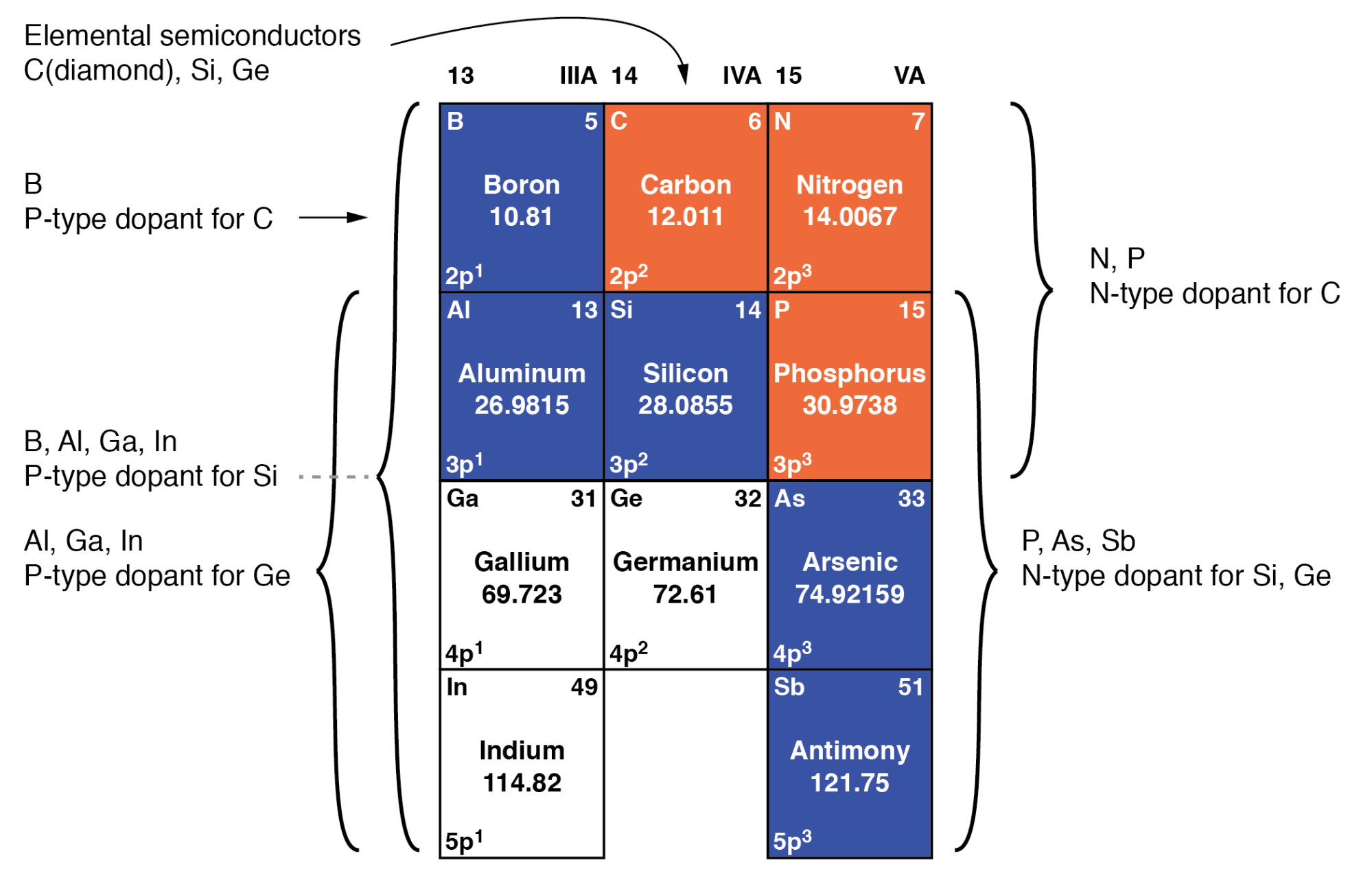
Doping
Doping is when we add impurities to the extremely pure silicon. This changes the electrochemical properties of the silicon. Silicon is in group 4 of the periodic table. Like Carbon it makes nice solid bonds in 4 directions. By adding elements from the 3rd or 5th columns we can add extra electrons or extra positive charges (holes where there are no electrons).
The elements we typically use are Boron for p-type (positive holes) doping and Phosphorus or Arsenic for n-type (extra electrons) doping. Undoped silicon has a very low conductivity meaning it does not conduct electricity, but it looks metallic. By adding small amounts of dopants it can be made to be conductive, and the voltage on transistor gates can change it from being insulating to conducting by controlling the way the extra (for N type) or missing (for P type) electrons behave.
The Arsenic is the poison in this fun tweet:
computers think using etchings in poisoned sand and measure time using vibrating crystals so if you were looking for magic you found it
— Computer Facts (@computerfact) April 20, 2016
For more information check this article from technocrazed
Course feedback
The fastest way I know to get 'behind the scenes' and learn how analog ASIC design and implementation really works. This was one of the most educational three months I've ever had.
Bruce MacKinnon (analog course)